Pharma overtakes vehicles on Australia's road to export success
This article was originally published in Scrip
The pharmaceutical industry was Australia's largest exporter of high-technology goods in 2008-09, accounting for A$4 billion ($3.6 billion) in exports, a new report has revealed.
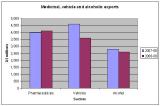
Medicinal and pharmaceutical products exports have now overtaken those of road vehicles, as the dominant export sector for the country, according to the first edition of Medicines Australia's Facts Book, a compilation of data on hi-tech and knowledge intensive industries. The latter totalled A$3.6 billion during the same period.
Exports of pharma products from Australia have grown significantly over the past six years, increasing in value from just under A$2.5 billion in 2003-04. Compared to the road vehicles and alcohol sectors, two other high-ranking export sectors, the pharmaceutical sector was the only one to see it exports grow continuously year on year. For example, while pharma exports were just under A$4 billion in 2007-08 and continued to climb, reaching more than $4 billion for 2008-09, vehicle and alcohol exports conversely fell between 2007-08 and 2008-09 by around A$1 billion and A$700 million, respectively.
Source: Australian Bureau of Statistics, Catalogue 5368.0, International Trade in Goods and Services, Australia 2007–08, September 2009
global markets
According to the Australian Bureau of Statistics, key markets for Australian pharma exports in 2007 were South Africa and New Zealand, generating A$455 million and A$448 million, respectively. The UK was Australia's sixth-highest grossing export market (A$202 million) and the US its 10th (A$140 million).
global markets
Pfizer's Lipitor (atorvastatin) was the top global product in 2008 (with sales of US$13.7 billion), followed by Bristol-Myers Squibb's Plavix (clopidogrel, $8.6 billion), AstraZeneca's Nexium (esomeprazole, $7.8 billion), GlaxoSmithKline's Seretide (fluticasone propionate plus salmeterol xinafoate, $7.7 billion) and Amgen/Wyeth's Enbrel (etanercept, $5.7 billion).
This was mirrored in medicine dispensing within Australia over the same period; Lipitor was the most dispensed drug with 9.8 million prescriptions issued, followed by Nexium, (4.7 million). Other high-ranking medicines included simvastatin (5.3 million) and atenolol (2.9 million). For highly-specialised drug programmes, HIV/AIDS antiretrovirals had the highest number of listed medicines in the country with 23; immunocompromised conditions had 10, hepatitis B or C agents had nine and immunosuppressive agents had seven.
PBS reforms
Throughout 2007-8, medicines in Australia were mainly funded by the government, which contributed 83% of the cost of the Pharmaceutical Benefits Scheme's listed medicines. This is the most the government has invested in the PBS over the past five years.
During 2009, Australia began to address a number of health system reforms. In July, the National Health and Hospitals Reforms Commission issued its report, A healthier future for all Australians, which made 120 recommendations to reform Australia's universal health care system, including prevention and early intervention and the introduction of patient-controlled electronic health records (scripnews.com, July 28th, 2009).
The report did not, however, propose any major reforms for the funding of medicines under the PBS. Earlier in the year Medicines Australia confirmed that it was continuing to "maintain" PBS growth, which sprung up to 1.8% in real terms over the three years to 2009, compared with 6.5% over the past 50 years (scripnews.com, April 30th, 2009).
The top companies on the PBS in 2007-08, by sales, were Pfizer (A$743 million), AstraZeneca (A$546 million), Sanofi-Aventis (A$415 million), GlaxoSmithKline (A$324 million) and Australian generic company Alphapharm (A$316 million). Other high sellers included Merck Sharp and Dohme (A$233 million), Bristol-Myers Squibb (A$199 million) and Lilly (A$195 million), the Department of Health and Ageing's Pharmaceutical Benefits Pricing Authority Annual Report 2007-08 reported.
In terms of global markets in 2008, Asia, Africa and Australia held 1.7% of the pharma market. North America by far dominated with 40.3%; this was followed by Europe with 32.0%, Japan with 9.9% and Latin America with 6.0% (IMS Health, Market Prognosis March 2009 figures).